Previously, GW researchers invented a method to selectively kill cancer cells with cold atmospheric plasma (CAP), while leaving neighboring normal cells unaffected. In the present invention, the researchers devised an enhanced method for CAP cancer therapy by concurrently exposing the cancer cells to a static magnetic field (Fig. 1).
The researchers demonstrated through in vitro experiments that when the cancer cells are placed in a magnetic field, the magnetic field increases the cancer cell death in response to CAP exposure (Fig. 2). This enhanced CAP cancer therapy can potentially provide an even more effective way to target and kill cancer cells.
The original CAP therapy device has been used on a human patient under a therapeutic use exemption to treat the area where a tumor was surgically removed, in order to kill any tumor cells that may have been left behind and prevent remission. Submission for FDA approval of the CAP device is anticipated in 2016.
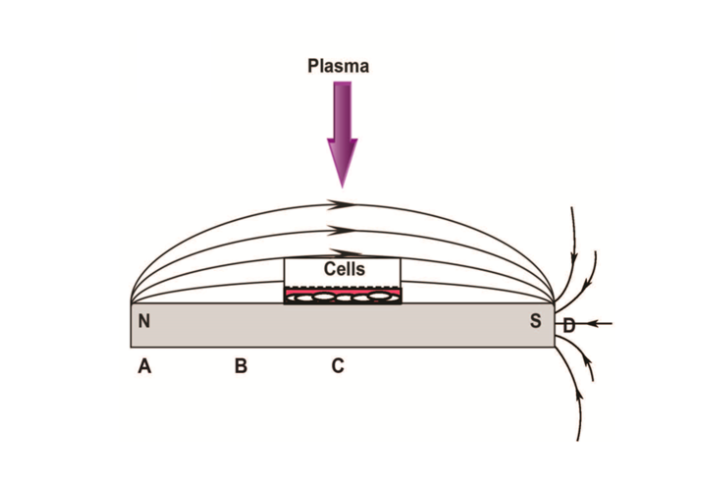
FIG. 1 - A schematic diagram showing cancer cells being subjected to cold atmospheric plasma while being placed in static magnetic field.
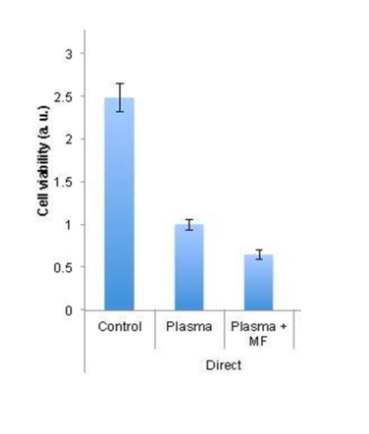
FIG. 2 - Static magnetic field enhances plasma-mediated killing of cancer cells.
Applications:
Cancer therapy
Advantages:
Enhanced cancer cell killing compared to CAP treatment alone